drosophila testis|Single : Tagatay Single-cell RNA-seq of Drosophila miranda testis reveals the evolution and trajectory of germline sex chromosome regulation. Kevin H-C. Wei, Kamalakar Chatla, . Resultado da The Inglis Sires', registered as the Sires Produce Stakes, is an Australian Turf Club Group 1 Thoroughbred horse race for two-year-olds at Set Weights run over a distance of 1,400 metres at Randwick Racecourse, Sydney, Australia in April during the ATC Championships Carnival. The prize .
0 · The stem cell niche: lessons from the Drosophila testis
1 · The stem cell niche: lessons from the Drosophila testis
2 · Testis single
3 · Structure and molecular basis of spermatid elongation in the
4 · Somatic cell lineage is required for differentiation and not
5 · Single
6 · Reproductive ecology of Drosophila
7 · Mitochondrial fusion regulates lipid homeostasis and
8 · Hedgehog in the Drosophila testis niche: what does it do there?
9 · Endocrine network essential for reproductive success in Drosophila
10 · Dynamic sex chromosome expression in Drosophila male germ
11 · Drosophila Pif1A is essential for spermatogenesis and is the
WEBAcompanhantes de Araçatuba. chegou há 2 dias. Ágatha Rios Araçatuba, SP, Brasil. Anúncios Básicos. Mostram o rosto. Alice Paes Araçatuba, SP, Brasil. Sayuri Kazzan .
drosophila testis*******We map the function of Drosophila Pif1A during spermatogenesis, showing that Pif1A is essential for spermatide individualization and involved in the regulation of the lipid metabolism genes. The Drosophila testis niche contains two stem cell types (i.e. GSCs and CySCs), the behavior of which is coordinately regulated by both local and systemic .
Single-cell RNA-seq of Drosophila miranda testis reveals the evolution and trajectory of germline sex chromosome regulation. Kevin H-C. Wei, Kamalakar Chatla, . Mitochondrial fission regulates germ cell differentiation by suppressing ROS-mediated activation of Epidermal Growth Factor Signaling in the Drosophila larval testis. SPATA33 is an autophagy. To capture the transcriptional profiles of the cell types in the Drosophila L3 testis, we dissected staged male third instar larvae, enzymatically removing the . To investigate the expression patterns of genetic novelties across cell types, we performed single-cell RNA-sequencing of adult Drosophila testis. We found that . Spermatid elongation is a crucial event in the late stage of spermatogenesis in the Drosophila testis, eventually leading to the formation of mature sperm after .
Reports of independent observations from three research groups have uncovered an important role of Hedgehog (Hh) in the Drosophila testis niche. In this review, we .SingleIn the Drosophila testis, germline and somatic stem cells are housed together in a common niche, where they are regulated by local signals, epigenetic mechanisms and .In testes, so-Drosophila matic cyst stem cells (CySCs) and the apical hub form the niche for neighboring germline stem cells (GSCs), with CySCs as the proposed source of .
Somatic cell lineage is required for differentiation and not maintenance of germline stem cells in Drosophila testes Jaclyn G. Y. Lima and Margaret T. Fullera,b,1 Departments of aDevelopmental Biology and bGenetics, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA 94305 Contributed by Margaret T. Fuller, September 23, 2012 (sent for review May .
In Drosophila melanogaster testes, the germline differentiation program must coordinate with germline stem cells (GSCs) self-renewal, and meiosis must take place at the appropriate time during .
The testis is a peculiar tissue in many respects. It shows patterns of rapid gene evolution and provides a hotspot for the origination of genetic novelties such as de novo genes, duplications and mutations. .
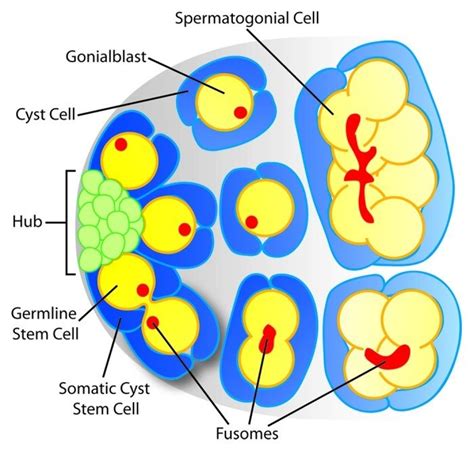
The adult Drosophila testis contains a well-defined niche created by a cluster of hub cells, which secrete signals that maintain adjacent germline stem cells and somatic cyst stem cells (CySCs). Hub cells are normally quiescent in adult flies but can exit quiescence, delaminate from the hub and convert into CySCs after ablation of all CySCs.

Schematic and representative testes of the genotypes used for the microarray experiments. (A) Schematic of the Gonial Proliferation Center (GPC) of a Drosophila testis. Germline stem cells (GSCs; red) are found adjacent to the hub (green) and are encased by two cyst progenitor cells (yellow).
In Drosophila, Witt et al. generated an adult Drosophila testis atlas by scRNA-seq and identified a cluster of lineage-specific de novo genes, elucidating the distribution of lineage-specific de .
drosophila testis Distribution of transcripts in different region of testis and analysis of the RNA-Seq results. a Distribution of Drosophila melanogaster transcripts by RNA-Seq. b Number of genes showing significant differences (FDR-corrected p-value< 0.05) in transcript level between different region of testis.c The combined number of transcripts and the .drosophila testis Single Distribution of transcripts in different region of testis and analysis of the RNA-Seq results. a Distribution of Drosophila melanogaster transcripts by RNA-Seq. b Number of genes showing significant differences (FDR-corrected p-value< 0.05) in transcript level between different region of testis.c The combined number of transcripts and the . At the tip of the Drosophila testis (apex) is a germinal proliferation centre, which contains the germline stem cells (GSCs) and somatic stem cells (CySCs) that maintain spermatogenesis 34,35,36 . The testes of Drosophila melanogaster provide an important model for the study of stem cell maintenance and differentiation, meiosis, and soma-germline interactions. Testes are typically isolated from adult males 0-3 days after eclosion from the pupal case. The testes of wild-type flies are easily distinguished from other tissues because they . 1. Introduction. Drosophila provides an excellent model for the characterization of functional genes contributing to male fertility [1,2].More than 10% (approx. 1500 genes) of mutations in the Drosophila genome are associated with male fertility [3,4].Spermatogenesis is a complex and highly regulated cell differentiation .
2. The Drosophila testis. Organogenesis of the Drosophila testis, a structure first made by the coalesce of germ cells and somatic gonadal cells in late embryogenesis, proceeds continuously throughout embryonic and larval stages, to reach maturation in adult stages. The embryonic gonad results from the coalescence of the . The adult Drosophila testis contains a well-defined niche created by a cluster of hub cells, which secrete signals that maintain adjacent germline stem cells and somatic cyst stem cells (CySCs). Hub cells are normally quiescent in adult flies but can exit quiescence, delaminate from the hub and convert into CySCs after ablation of all CySCs. In the Drosophila testis, this was largely the case for germ cells early in the differentiation lineage (Figure 4G and H). In contrast, comparing these two approaches for later stage germ cells revealed a striking difference, reflecting an important aspect of testis biology. Our data show that directly comparing sn- to scRNA-seq can highlight .
Drosophila male germline stem cells (GSCs) reside at the tip of the testis and surround a cluster of niche cells. Decapentaplegic (Dpp) is one of the well-established ligands and has a major role .
We map the function of Drosophila Pif1A during spermatogenesis, showing that Pif1A is essential for spermatide individualization and involved in the regulation of the lipid metabolism genes.
The Drosophila testis niche contains two stem cell types (i.e. GSCs and CySCs), the behavior of which is coordinately regulated by both local and systemic signals to produce the precise ratio of germline and somatic . Single-cell RNA-seq of Drosophila miranda testis reveals the evolution and trajectory of germline sex chromosome regulation. Kevin H-C. Wei, Kamalakar Chatla, Doris Bachtrog
Mitochondrial fission regulates germ cell differentiation by suppressing ROS-mediated activation of Epidermal Growth Factor Signaling in the Drosophila larval testis. SPATA33 is an autophagy. To capture the transcriptional profiles of the cell types in the Drosophila L3 testis, we dissected staged male third instar larvae, enzymatically removing the associated fat body before . To investigate the expression patterns of genetic novelties across cell types, we performed single-cell RNA-sequencing of adult Drosophila testis. We found that new genes were expressed in various cell types, the patterns of which may be influenced by their mode of origination. Spermatid elongation is a crucial event in the late stage of spermatogenesis in the Drosophila testis, eventually leading to the formation of mature sperm after meiosis. During spermatogenesis, significant structural and morphological changes take place in a cluster of post-meiotic germ cells, which are enclosed in a microenvironment surrounded .Reports of independent observations from three research groups have uncovered an important role of Hedgehog (Hh) in the Drosophila testis niche. In this review, we summarize these recent findings and discuss the interplay between the Hh signaling mechanisms and those of the JAK-STAT and BMP pathways.
14 de dez. de 2021 · Billie Eilish s’est confiée sur sa sexualité et son rapport à la pornographie dans l’émission «The Howard Stern Show». Billie Eilish s’est confiée à .
drosophila testis|Single